Surgical positioning is the practice of placing a patient in a particular physical position during surgery. The goal in selecting and adjusting a particular surgical position is to maintain the patient's safety while allowing access to the surgical site. Often a patient must be placed in an unnatural position to gain access to the surgical site.
It is generally used for head, face, chest, abdomen and limb surgery.
Application: The most common surgery, such as abdominal surgery, some gynecological and orthopedic surgery
Horizontal supine position: surgery on chest, abdomen, lower limbs, etc.
Supine position with head down: suitable for thyroid, anterior cervical surgery, cleft palate repair, general anesthesia, tonsillectomy, tracheal foreign body, esophageal foreign body and other operation
Oblique supine position (45 degrees): suitable for anterior lateral approach, lateral chest wall, axillary surgery, etc.
Side head supine position: suitable for ear, maxillofacial, side neck, head and other operation
Upper limb abduction supine position: suitable for upper limb and breast surgery
It is often used for back and lumbosacral surgery.
Application: For all operations from the back (including cervical spine, posterior, rectal area and back limbs)
It is used for chest incision surgery and hip surgery.
The lateral position is a commonly used clinical surgical position, which is often used for neurosurgery, thoracolumbar surgery, and hip surgery.
Advantages: It has the advantages of sufficient exposure of the surgical field and convenient operation by the surgeon.
Disadvantages: The lateral position may cause changes in the patient's physiology, which can easily lead to complications such as circulation, breathing disorders, nerve damage and skin bedsores.
General surgery chest lateral position: suitable for lung, esophagus, side chest wall, side waist (kidney and ureter middle and upper part) surgery, etc.
Lateral position for kidney and ureter middle and upper section surgery: 3cm from the lower rib to the lumbar bridge, suitable for kidney surgery, nephrectomy, ureteral stone removal (without lumbar bridge, "folding bed" is the flex position).
Lateral position for hip surgery: suitable for acetabular fracture combined with posterior dislocation of the hip, artificial hip replacement, quadratus femoris bone flap transposition for the treatment of aseptic necrosis of the femoral head, open reduction and internal fixation of femoral shaft fractures, and femoral tumors , Femoral neck fractures or intertrochanteric fractures, internal fixation and upper femoral osteosynthesis, etc.
It is often used for anal or perineal surgery.
Application: Maximum exposure of the perineum, mostly used for anorectal surgery and gynecological surgery
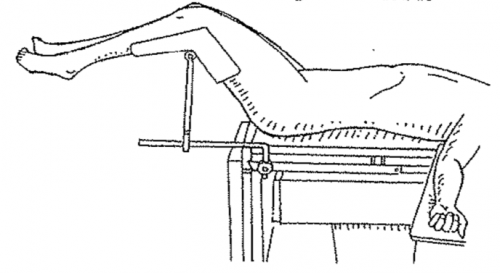
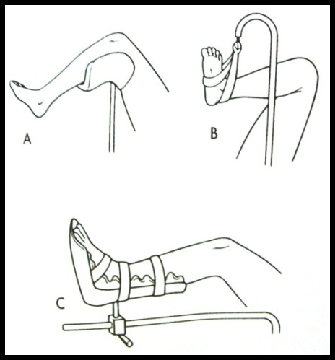
Low leg stirrup position: Local force is more even (but too high can cause severe back pain)
Middle lithotomy position knee crutch: Compression of the common peroneal nerve causes foot drop and nerve damage
High lithotomy position leg holder: plantar nerve damage, excessive bending, sciatic nerve damage

It is often used for head and neck surgery.
The variation of the supine position, sometimes accompanied by a small downward fold of the leg plate.
Application: often used for laparoscopic surgery, or pelvic or lower abdomen surgery

The patient's posture should be able to move to the supine position under normal conditions or even emergency situations where the power supply is interrupted.
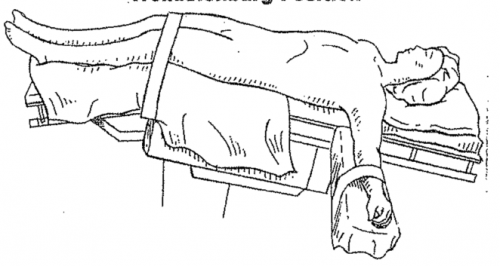
Supine position with head down, also known as Trendelenburg position (Trendelenburg), is a patient position commonly used in clinical practice. It has certain clinical significance for the patient's breathing and blood circulation. It is often used to treat early hypotension It is also used to treat air embolism, and even as an emergency rescue measure for shock.
It is often used for head and neck surgery.
Application: commonly used in head and neck surgery to reduce venous congestion and prevent gastric reflux during the induction of anesthesia
Special attention: backward tilt is Trendelenburg, forward tilt is reverse-trendelenburg

It is used for rectal surgery.
Application 1: In gallbladder and kidney surgery, in the absence of a lumbar bridge, the back and buttocks are folded to form an arch to replace the lumbar bridge.
Application 2: Gluteal muscle and anal (rectal) surgery
Disadvantages: The arch starting point is fixed, and the height is limited by the folding angle.



 沪公网安备31011802003750号
沪公网安备31011802003750号